Review of Large City & Metropolitan Area power system development trends taking into account new generation, grid and information technologies
The number of Large Cities & Metropolitan Areas (MA&LC) is increasing both in size of population and in surface area. Accordingly, electricity consumption and power system (PS) load are growing and are concentrated in densely populated areas. In addition, MA&LC are important political and economic centres, and loss of load, or even load curtailment, can have a significant financial impact on companies and consumers. The safety and reliability of power systems must endure when facing today’s challenges such as RES integration, energy transition, capacity and power balancing adequacy, restoration and modernization of the networks, and the installation of new generating and power system equipment.
Members
Convenor (RU)
S. UTTS
Co-Convenor (BR)
V.S. DE JESUS
M. LUND (CA), S.CURLIN (HR), L. ZHONG (CN), P. FUNGWITHTAYA (TH), N. HATTORI (JP), L. LEITE (BR), Z. MA (CN), M. MONDELLO (US), D. MUSHAMALIRWA (FR), P. VAN OIRSOUW (NL), D. PILENIEKS (RU), J. PILLAI (DK), C. REALI (CA), H. SARMIENTO (MX)
Corresponding Members
A. RAMDHIN (ZA), S. SAGARELI (US), Z. LIDONG (SE), A. BIANCO (BR), X. XIALING (CN), C. MARTINS LUIZ (BR), B. COVA ( IT), F.F. AGUEDA RUIZ (ES), J. ARANEDA (CL), S. WEERASINGHE (UK)
Special Thanks to Respondents
C. CHRISTODOULOU (GR), Z. REN (CN), C. AKSAKAL (TR), Y.B. YOLDAS (TR), L.M. ALVES (PT), M. KOENIG (US), R. DE DIOS ALIJA ( ES), E. LLORENTE MIGUEL (ES)
Scope/Methodology:
The role of this CIGRE JWG is to:
- Discuss the development trends that are influenced by RES integration, energy transition, consumption and load values, generating capacity, and grid development in MA&LC power systems; and
- Identify the most commonly used solutions, such as, new generating, grid and information technologies that can address development trends.
This Technical Brochure, which is the result of the work of 34 members and respondents, launched new directions of study to investigate MA&LC power systems as separate power systems with their own characteristics and features.
Description of TB
The Technical Brochure is organized into six chapters:
- Introduction
- Scope and definitions
- Questionnaire survey - main highlights
- Large city & metropolitan area power system development trends
- Power system technologies in large city & metropolitan areas
- Conclusions and further recommendations
Preliminary definitions of Metropolitan Area power systems and Large City power systems were discussed on chapter 2. It was adopted that Metropolitan Area power system means the regional power system of the country’s capital city, consisting of a densely populated urban and suburban territory with industry and domestic consumers. The population of Metropolitan area is usually more than 3 million. people, and peak load usually more than 5 GW.
Large City power system means a city power system including densely populated urban territory with industry and domestic consumers. The population of a large city is usually more than 1 million people, and peak load usually more than 2 GW.
With the aim to find basic MA&LC power systems characteristics and trends, a Questionnaire Survey (QS) was launched and summarised on chapter 3.
The concluded MA&LC power systems problems and technologies are presented on Figure 1.
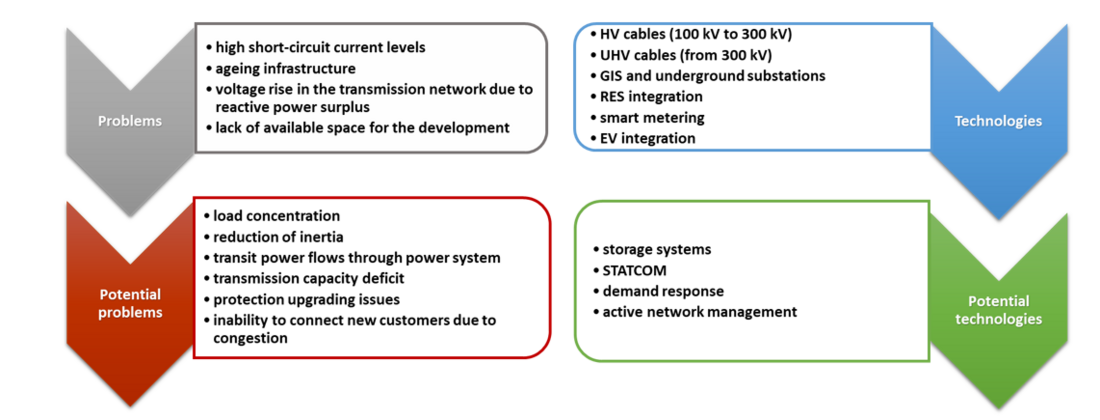
Figure 1 - Problems and technologies (existing and potential) based on Questionnaire Survey
The results of this questionnaire were the input data for further analysis about development trends and power system technologies.
The fourth chapter presents conclusions about MA&LC power system development trends. Development trends, energy transition drivers, issues and trends are studied and presented in detail, including hydrogen development, heat decarbonization, technical trends etc. Moreover, correlation between development trends and planning process and reliability issues is introduced. It was concluded that a dedicated MA or LC power system development plan is needed to ensure adequate planning processes and coordination with all utilities on a city level to achieve all energy transition goals. Several MA&LC power systems development plans are presented. Reliability issues and resilience play a significant role in MA&LC power systems in the energy transition era.
The fifth chapter presents information about power system technologies in MA&LC power systems based on problems and trend that are identified in previous chapters.
The first technology area covers renewable energy sources, dispersed generation, and storage integration in MA&LC power systems. Based on delivered projects and real experience, the most efficient implementation of such technologies in MA&LC power systems is identified. Conclusions about the effective volume of renewable energy sources, dispersed generation, and storage in MA&LC power systems, and the corresponding transmission and distribution grid developments, are presented. The generating structure should be such as to avoid the risk of blackout and with the aim to provide sustainable and reliable power supply.
A number of MA&LCs set targets of 100% RES generating capacity by 2030, 2040, or 2050. In the view of this JWG, these targets cannot be achieved in near future without the following actions:
- Integration of large wind and solar power plants with a rated generating capacity greater than the peak load of the MA&LC power system, taking into account the installed capacity utilization factor,
- Installation of the necessary number of interconnections;
- Transmission and distribution grid reinforcements and upgrades;
- Provision of the necessary level of observability;
- Modernization of emergency control and system protection schemes; and
- Providing adequate amounts of frequency reserve and balancing.
The role of conventional generation in future MA&LC power systems should be assessed also for cities which need a heat supply using district heating or other solutions.
The second technology area is dedicated to HVDC and FACTS device integration in MA&LC power systems. The application of HVDC and FACTS technology is considered in response to increasing generation in high load density grids and, or the growing interconnections between power systems.
The third technology area covers the application of cables, modern OHLs, GIS, GIL, and underground substations in MA&LC power systems. It concludes that all of the described technologies should be developed and assessed as part of the power system development planning process. The resilience issue and nature disasters should be also considered.
The fourth technology area considers smart grid and demand response implementation in MA&LC power systems. The capability of each smart grid technology application in MA&LC power systems is assessed. Equally, the range of types of consumers and of demand response service provision are considered. Real examples of smart grid and demand response are presented.


