Mechanical properties of insulation materials for power transformers
Solid insulation materials are crucial for the functional and long-term performance of power transformers; these include for example, paper, pressboard, laminated wood, aramid-based components. Beyond their role as dielectric materials, their ability to sustain mechanical loads is equally important. Recent advances in materials science, testing, and modelling have significantly improved our understanding of the mechanical behaviour of insulation materials. The D1.65 brochure provides an overview of the current state of the art, focusing on liquid-filled power transformers, while excluding materials for special applications such as gas-insulated power transformers.
Members
Convenor (DE)
L.E. SCHMIDT
L. BOIRON (FR), M.-L. COULIBALY (FR), F. ERENLER (TR), O. GIRLANDA (SE), L. HEAN (CN), P. HEINZIG (CH), D. MARTIN (REVIEWER, AU), S. MUMCU (TR), Y. ODARENKO (AU), S. ÖSTLUND (SE), H. NIEHOFF (DE), Á. PORTILLO (UY), M. RYADI (FR), J. TUSEK (REVIEWER, AU), K. ZAFEIRIS (DE), X. ZHANG (CN)
Introduction
While the dielectric performance and aging of solid insulation for power transformers are well-documented in the literature, there is a relative scarcity of publications addressing mechanical properties. Many contemporary testing methods described in standards relate to typical material characteristics. However, properties specific to application requirements, such as mechanical strength and compression stiffness, are less frequently covered. The development of novel mechanical simulation methods and the higher mechanical stresses encountered in specific applications, such as transformers for electric arc furnaces, have underscored the importance of understanding the mechanical behaviour of these materials.
The brochure begins with an overview of the materials used for insulation in power transformers. Understanding the main materials and their production processes is essential for comprehending material behaviour and its function in power transformers.
Next, it explores the general mechanical requirements that solid insulation materials in power transformers must meet to ensure safe operation. This includes distinguishing between standard operation and special conditions such as short circuits. Following this, the brochure delves into important material properties, examining how factors such as moisture and temperature influence mechanical properties. One important aspect not covered is material aging, as this has been comprehensively addressed by other CIGRE working groups for example CIGRE Technical Brochure 738 [1].
Innovative testing approaches are then introduced. Some of these methods may eventually be incorporated into technical standards, while others are intended for research purposes.
Finally, the brochure highlights recent advances in mechanical simulation for example more complete material models. These simulations enhance our ability to predict mechanical insulation behaviour and optimize design. By integrating insights from these sections, engineers and researchers can make informed decisions to enhance power transformer insulation and ensure reliable, long-lasting operation.
Insulation materials used in power transformers
In power transformers, many solid insulation materials are fibre-based, such as pressboard, paper, and fibre composites. Additionally, some raw materials naturally contain fibres, like the veneers used in laminated wood or the cellulose fibres used in the production of pressboard or paper. Fibre orientation significantly impacts the mechanical properties, creating complex characteristics. Unlike many common materials that are isotropic—having uniform properties in all directions and requiring testing in only one direction (e.g., structural steel)—the mechanical properties of typical insulation materials like paper, pressboard, laminated wood, and aramid paper depend on the direction of the applied loads.
The fibre orientation in the materials is linked to the production method. On a paper machine for example the fibres are aligned to a certain degree with the operating direction of the paper machine (see Figure 1). The tensile properties of the paper are therefore the highest in machine direction.
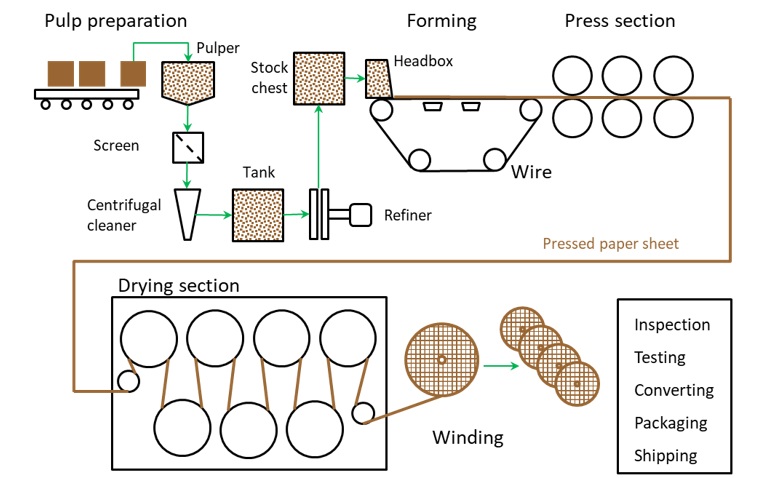
Figure 1 - Illustration of insulation paper manufacturing
Important considerations in power transformers
Power transformers are designed to withstand mechanical stresses encountered during normal operation and events such as short circuits or inrush currents. Solid insulation plays a critical role in insulating components within the transformer, maintaining spacing in electrically stressed oil ducts, and facilitating liquid flow for cooling. Additionally, it enhances the mechanical stability of transformers during transport, regular operation, and extraordinary events like short circuits....


