Overhead lines
by Herbert Lugschitz, Chairman & Wolfgang Troppauer, Secretary
Study Committee B2 covers the design, construction and operation of overhead lines. This includes the mechanical and electrical design and experimental validation of new line components (e.g. conductors, ground wires, insulators, accessories, structures and their foundations), the study of in-service line performance and assessment of aged line components, line maintenance, the refurbishment and life extension as well as upgrading and uprating of existing overhead lines.
Overhead lines play an important role for the Power System of the Future and its challenges. The activities of SC B2 are full in line with this important aspect of CIGRE´s mission.
B2 has Regular Members from 24 countries, 2 Regular Additional Members, Observers from 17 countries, and 7 Advisory Groups which coordinate.
The Technical Direction of SC B2 is:
- Increase the ampacity of existing lines
- Ensure reliable lines, or establish / improve the reliability of existing lines
- Ensure environmentally compatible lines
- Assessment of lines, methods, new tools
SC B2 cooperates with SCs B1 “Insulated Cables” and C3 “Power system environmental performance”. Environmental aspects are getting more and more important and the close relationship we developed with C3 makes the work of B2 and C3 more pertinent. The cooperation with C1 has the main goal to inform about actual developments and tendencies. B2 has “ambassadors” which take part at the Technical Meetings of B1 and C3, and vice versa.
The main highlight in 2019 was the B2 Annual Meeting in Delhi/India, in combination with the International Joint Colloquium A2, B2, D1. Three Technical Sessions were organized and chaired by B2:
- Design Optimization new lines,
- Reliability and Economics, Maintenance
- New Materials and Products for use on OHL, Diagnostics
Working Groups
End of December 2019 SC B2 consisted of 22 Working Groups, 478 experts contributed in WGs (excluding multiple memberships in different WGs), from 48 countries. B2 has app. 7 % female members in WGs.
Technical Advisory Groups
The four Technical Advisory Groups (TAGs) provide advice for assisting the Chairman in the definition of the technical directions to be followed by the SC. The four TAGs cover:
- Electrical aspects (TAG04)
- Tower, foundations and insulators (TAG05)
- Mechanical aspects (TAG06)
- Asset Management, Reliability, Availability (TAG07)
Their responsibilities are:
- To coordinate WGs within the scope of the relevant TAG
- To identify future direction of the technology in the field of their technical area
- To prepare new items of work and to submit them to CAG and SC Chairman
- To coordinate and promote tutorials covering their scope of work
- To attract new Members and retain existing Members
Technical Advisory Group “Electrical Aspects” TAG04
WG B2.59 Forecasting dynamic line ratings
Many documents have recognized the advantages of calculating variable line ratings based on real-time weather measurements in the line corridor since such ratings are typically well above static line ratings. The WG explores methods that allow both short-term and medium-term forecasting of variable/dynamic line ratings to encourage use by system operations.
WG B2.62 Compact HVDC overhead lines
This WG undertakes studies leading to greater compaction of DC lines in order to reduce their visual and environmental impact and to allow their construction on narrower rights of way. It is recognized that the electrical, mechanical and environmental constraints associated with compact HVDC lines differ from those associated with HVAC lines, which is considered in the key issues of the paper.
The TB is expected in the 2nd half of 2020.
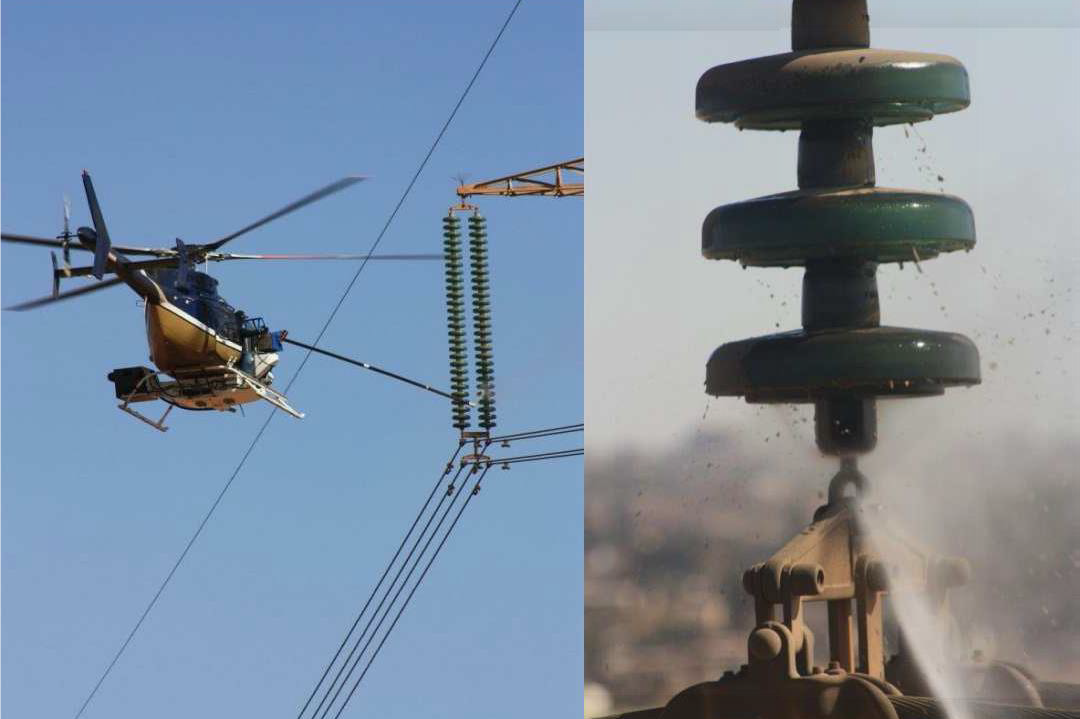

Compact lines live maintenance activities:
Helicopter based aerial washing of insulators under live conditions
WG B2.63 Compact AC overhead lines
The objective is to identify the balance between reduction in phase-to-phase spacing and structure height with the need to perform routine maintenance without taking these lines out of service. The scope includes finding ways to maximize their emergency power flow capacity to handle occasional but severe post-contingency loads. Line design parameters like corona, bundle design (expanded, asymmetrical), audible noise and radio Interference, overvoltage (switching and lightning surges), live line maintenance clearances, conductor mechanical parameters are studied.
The TB is expected in spring 2020.
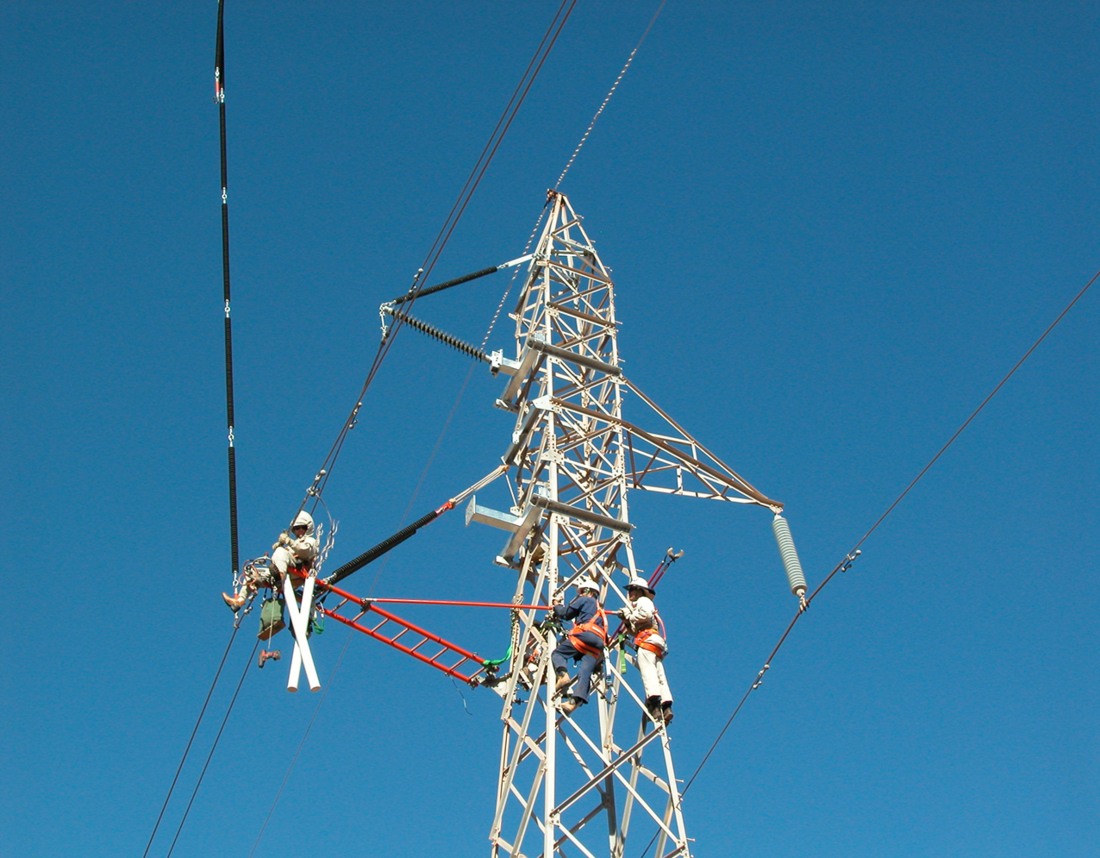

Live line work on an overhead line
(J. McCormack, A. Milne, D. Lammers, “Review of Safe Work Guidelines” at International Colloquium on Latest Trends & Innovations on Overhead Lines)
New 2019: JWG B2/C4.76 Lightning & Grounding Considerations for Overhead Line Rebuilding and Refurbishing Projects, AC and DC; lead B2
Line refurbishment options include replacement or refurbishment of the key components of the overhead line, namely structures, foundations, insulators including fittings, conductors and overhead ground wires, and grounding. All of these components affect the lightning performance, if altered.
The lightning performance of overhead transmission and distribution lines can significantly affect overall reliability of supply. Technical studies and literature have addressed individual subjects, such as, lightning parameters, remedial measures, line lightning performance, etc. for many decades. There is a need for a coordinated approach to grounding design, considering both lightning and power system fault management. The objective of the work will be to add value to transmission and distribution line replacement / reconductor / refurbishment projects by modifications in the redesign process.
Technical Advisory Group “Tower, foundations and insulators” TAG05
WG B2.57 Survey of Operational Composite Insulators Experience & Applications
An application guide for composite insulators for voltage levels > 100 kV is being developed. It takes into consideration the actual status of international product standards as well as application cases, which are not yet covered by standards. The guide will cover all types of composite line insulators and their electrical and mechanical aspects. An important part of the document is the identification whether gaps exist between existing standards and the state-of-the-art used in service.
WG B2.61 Transmission Line Structures with Fibre Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Composites
Fibre Reinforced Polymer materials have considerable durability, environmental friendliness, timely structure delivery and good quality material availability. In the last years FRP has become common in the aerospace, military, shipping, car, civil engineering and sports gear industries and replaces traditional materials. Such composites are also used for overhead line poles, cross arms, cross bracings and other structural components. Other fibre reinforcements for example carbon fibre, aramid (Kevlar) and basalt fibre are also considered.
The TB is expected in the 2nd half of 2020
WG B2.65 Detection, Prevention and Repair of Sub surface Corrosion in Overhead Line Supports, Anchors and Foundations
Grillage type foundations, stay anchors, and direct embedded steel poles that involve direct steel to soil contact have been used successfully installed in many regions, but there is a number of instances where subsurface corrosion has made such applications inappropriate. This has resulted in failures, and/or expensive restoration of affected lines, e.g. in certain arid regions. The WG is preparing a report on the causes of subsurface corrosion, detection, prevention and repair of affected structures, anchors and foundations.
WG B2.67 Assessment and Testing of Wood and Alternative Material Type Poles
Wooden poles in many countries were considered to last many decades with regular inspection (5 - 10 year interval). In the past 20 years several issues have been found to exist with wood poles. Among them are, that poles can be conductive with linesman being endangered getting electric shocks - depending e.g. on the type of treatment. Poles were weakened through degradation. Poles may prove dangerous to climb; strong objection to the use of preservatives (e.g. creosote); the type of foundation - direct embedded or with some foundation; and whether the pole is guyed, also have an influence on the lifetime and potential failure mechanisms of a pole.
The WG determines the present status of wood pole experience and extent of failures in utilities worldwide and different types of timbers, define methods for testing and inspecting wood poles, methods to strengthen or reinforce degraded poles, provide guidance on the type of alternate pole materials, e.g. steel, concrete, composite and test methods. Fibre Reinforced Polymer (FRP) composite poles are not considered in this WG but are covered in WGB2.61.
Technical Advisory Group “Mechanical aspects” TAG06
WG B2.50 Safe handling. of fittings and conductors
Many problems experienced in the field of OHL conductors and fittings are due to poor handling and installation practices. A survey of current practice by manufacturers, contractors and utilities to ensure correct handling and installation of fittings and conductors has been carried out. The WG produces guidelines with the aim of promoting good practice to minimise handling and installation problems with fittings and conductors.
The TB is expected in the 2nd half of 2020


Left: shows damages on a conductor surface caused by the conductor drum during stringing works; Right: shows conductor birdcaging when pulling off the drum
WG B2.58 Vibration modelling of High Temperature Low Sag conductors – Self-damping characterization
The goal of this WG is modeling of aeolian vibrations of such conductors, including recommendations for laboratory tests on conductors and fittings. Based on the obtained results from such tests a methodology is being carried out to model conductor self-damping. This will assist overhead line engineers to improve line protection by better being able to predict line behavior with respect to aeolian excitation.
WG B2.66 Safe handling and installation guide for high temperature low sag (HTLS) conductors
The use of HTLS conductors has been increasing over the years. During installing these conductors, there is a risk of conductor damage which may lead to non optimal performance or failure. There is at present a lack of guidance in handling such conductors. The WG analyses the installation and handling of these conductors in greater detail especially in relation to IEEE 524 which is currently the most widely used standard on installation. The aim is to get more detailed feedback from various utilities, manufacturers and contractors that are currently handling these types of HTLS conductors. The WG is especially focusing on the composite cores and/or envelopes that require special handling. Guidelines are produced relating to handling of HTLS conductors based on practical experience and laboratory testing.
WG B2.68 Sustainability of OHL conductors and fittings – Conductor condition assessment and life extension
Many OHL throughout the world are nearing or have gone beyond their expected life. Since the conductors (including their installation) represent approximately 40% of the cost of the line, their condition is predominant in the decision to replace the line or extend its life after evaluating if they are degraded. The challenge is to prolong the residual life of the conductors without impacting the line reliability beyond what is acceptable to the Transmission System Operator. The interaction between conductors and fittings must also be considered since they are part of the same system. The topics that are covered in the Technical Brochure are corrosion, fatigue (thermal, electrical), inspection and test methods to prolong the life of the conductors and fittings, ongoing research and prospects, asset management (decisional chart on best practices to establish conductor condition, how to collect data from the field…). The WG covers only conventional conductors.
WG B2.70 Aircraft warning markers and bird flight diverters for Overhead Lines – Experience and recommendations
Aviation regulations require marking of overhead lines OHL in certain areas by means of aircraft warning markers. Besides, bird protection in sensitive areas requires enhancement of visibility of OHL for the birds by means of bird flight diverters. At present there is a lack of standards for requirements and tests of such visual warning fittings. The Technical Brochure gives guidelines regarding requirements and tests of these devices. The visual warning fittings include aerial markers for aerial navigation and water crossings. This WG´s recommendations can be the basis of a standard that sets the quality requirement in regards to materials, application, performance, required testing, and how to eliminate conductor and shield wire damage over the life of the system.
WG B2.71 Recommendations for Interphase Spacers of Overhead Lines
Interphase spacers have been used for over 40 years to prevent phase-to-phase contacts due to galloping and other conductor motions. Although their use is common, limited information has been published on technical requirements for such systems. The aim of this work is to assist line engineers to specify and select interphase spacers suitable for their application. This also concerns impacts on maintenance procedures when spacers are installed (including live-line methods).
New 2019: WG B2.75 Application guide for insulated and un-insulated conductors used on medium and low voltage overhead lines
Conductors used on overhead medium and low voltage systems may utilize insulated conductors. Each option has advantages and disadvantages, e.g. there may be fewer faults using insulated or covered conductors but permanent faults may be more difficult to locate. It is in the interests of utilities to understand the experiences of other utilities with respect to which type of network performs better than which and under which conditions. Networks included in this work are low voltage being less than 1000 V AC, and medium voltage from 1 kV to 45 kV AC.
Technical Advisory Group “Asset Management, Reliability, Availability” TAG07
WG B2.40 Calculations of the electrical distances between live parts and obstacles for OHL
A number of past SC B2 working groups have investigated and published reports relating mostly to “internal” or phase and circuit spacing. The present determines the extent below and along a line that may potentially be or is impacted by the line operation, and whether obstacles or activities within the influence of the line are considered to impact on the operation of the line itself. It is envisaged these impacts may comprise limitations for the line operation and or electrical current carrying capacity unless target “external” clearances and/or a defined protected width / area can be achieved.
The Technical Brochure is expected 2nd half 2020.
WG B2.60 Affordable Overhead Transmission Lines for Sub-Saharan Countries
This work explores the possibility to optimize Overhead Transmission Lines, with specific emphasis for African Sub-Saharan Countries, in terms of cost and reliability. Such infrastructures are capital intensive and, in what concerns the energy grid, sometimes require specialized manpower, not all of which often can be found in developing countries. Therefore, energy infrastructures projects, in particular the ones related to the transmission grid, are developed mainly through turn-key projects, financed by international organizations. Because many of these developing countries do not have national standards, infrastructure design follows international standards, leading to, sometimes, more expensive infrastructures and somewhat out of the local context.
WG B2.64 Inspection and Testing of Equipment and Training for Live-Line Work on Overhead Lines
Live-line maintenance of power lines is widely used worldwide at low, medium and high voltage levels. This work requires special tools to guarantee the maximal safety of the workers. All the equipment for live-line methods must undergo various inspections before use. These inspections could be type tests at the factory, acceptance tests before the first use, on-site tests before every use and periodic tests after a pre-defined period of time. Unfortunately, there is no common framework to define the different kinds of tests and their frequency.
Another important aspect is related to the education of workers. This WG would extend the JWG B2/B3.27 work, and further increase the awareness of live-line working requirements for equipment certification and personnel training.
WG B2.69 Coatings for Power Network Equipment
The last decade saw the development of a variety of surface engineering techniques and advanced coatings with properties like self-cleaning, icephobicity and anti-corrosion. These new technological advances can potentially benefit the power industry in reducing the risk of flashovers on insulators, corona losses and noise from conductors and fittings as well as mechanical problems caused by ice and snow accretion on overhead power networks. The WG will deliver mainly practical applications and remedies rather than theoretical studies and considerations. These results will include the review and identification of new practical and durable coatings as well as surface engineering techniques in order to increase the reliability of power networks in various environmental conditions as well as to respond to environmental concerns caused by corona noise and visual aspects of overhead power networks.
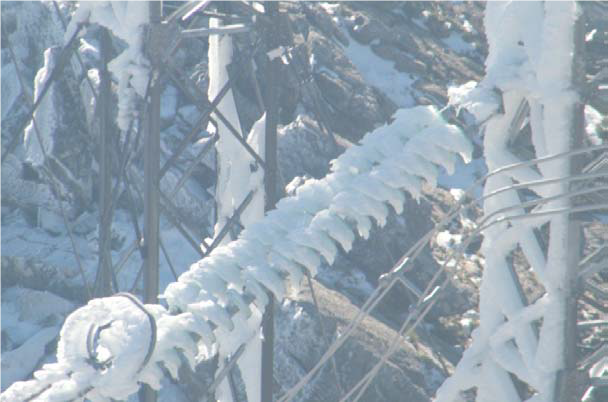

Snow/ice accreation on a strain insulator (not coated)
New 2019: WG B2.73 Guide for Prevention of Vegetation Fires Caused by Overhead Line Systems
Vegetation fires are a regular occurrence in many locations globally. They originate from natural, deliberate and accidental causes. A percentage of the accidental fire starts are associated with overhead distribution and transmission lines (e.g. contact of conductors with vegetation). The aim of this Working Group is to produce a Technical Brochure that will contain guidelines for preventing vegetation fire starts from overhead line assets. References respective cooperation exist with five other WGs of CIGRE.
New 2019: WG 2.74 Use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for assistance with inspection of overhead power lines.
UAVs have in recent years become available to assist with planned inspections of overhead lines and with emergency inspection. They have the potential to significantly improve efficiency of both tasks, by reducing the time needed to complete the tasks and for increasing the number of defects detected during the inspections. Practical questions of using UAVs in this application exist, e.g. when and how often to perform inspections, under which conditions and how they should be performed, and which UAV technologies are best suited to this application. Issues such as battery life and how to translate images into useful reports and legal requirements also need consideration. The work is also an update of TB 731 “The use of robotics in assessment and maintenance of overhead lines” regarding UAVs.
New 2019: JWG B2/D2.72 Condition Monitoring and Remote Sensing of Overhead Lines
Condition monitoring and remote sensing of overhead lines refer to real-time continuous monitoring of passages, operational status of lines and towers, operation type parameters of lines and meteorological conditions of corridors by adopting wireless data transmission. They help to operate overhead lines safely.
The growing number of lines, especially those in uninhabited remote areas, in several cases proves the traditional line inspection methods to be inadequate. Challenges arise in such areas like inconvenient transportation, operation and maintenance difficulties, complex equipment conditions and low inspection efficiency.
The WG will specify condition monitoring and remote sensing of overhead lines concerning the selection of installation sites, design, power supply, signal transmission and environmental situations of remote sensors. It also covers methods of acquiring, storing and analysing data, physical and cyber safety of the monitoring devices, tests and verification, and wide-area remote-sensing-based status detection. Other aspects are improving the level of monitoring the operational status, safety and reliability of the operation of a line.
Publications and Tutorial Group PTAG
Publications in 2019
Several B2 Working Groups finished in 2019 and published Technical Brochures.
Technical Brochure 767 "Vegetation fire characteristics and the potential impacts on overhead line performances" has been published in June 2019.
This Technical Brochure deals with the subject of vegetation fires under overhead lines. The brochure is the first document on this subject that deals with the subject as widely as possible and includes most of the disciplines involved in fire. It covers inter alia the financial implications of fire, safety aspects, breakdown of a gas during a fire, weather and fire tracking systems and also proposes a model for the breakdown during a fire. The document contains a long list of references as well as an appendix with the mathematical treatment of the breakdown as well as the conductivity of a flame. It is a document that will be of great value to anybody dealing with most aspects of fire.
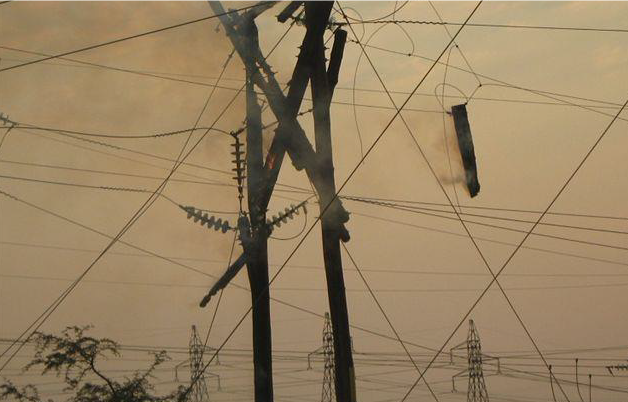

A failed wood pole structure caused by a grass fire in South Africa
Technical Brochure 763 "Conductors for the Uprating of Existing Overhead Lines" has been published in April 2019.
Renewable and distributed power generation is displacing conventional base load coal and nuclear plants. This often causes large shifts in power flow during both normal and emergency operation of the transmission system. As a result, certain existing AC overhead transmission lines may exceed their design thermal rating during either normal or emergency operation.
This brochure concerns methods of increasing the thermal rating of existing overhead lines by raising the maximum temperature of the original conductor or re-conductoring the line with larger or high-temperature, low-sag conductors while avoiding the replacement or extensive reinforcement of existing transmission structures. In most applications, the line structures must be in good or excellent condition, to use these uprating methods. The existing phase conductors, however, may be replaced with High-Temperature, Low-Sag (HTLS) conductors.
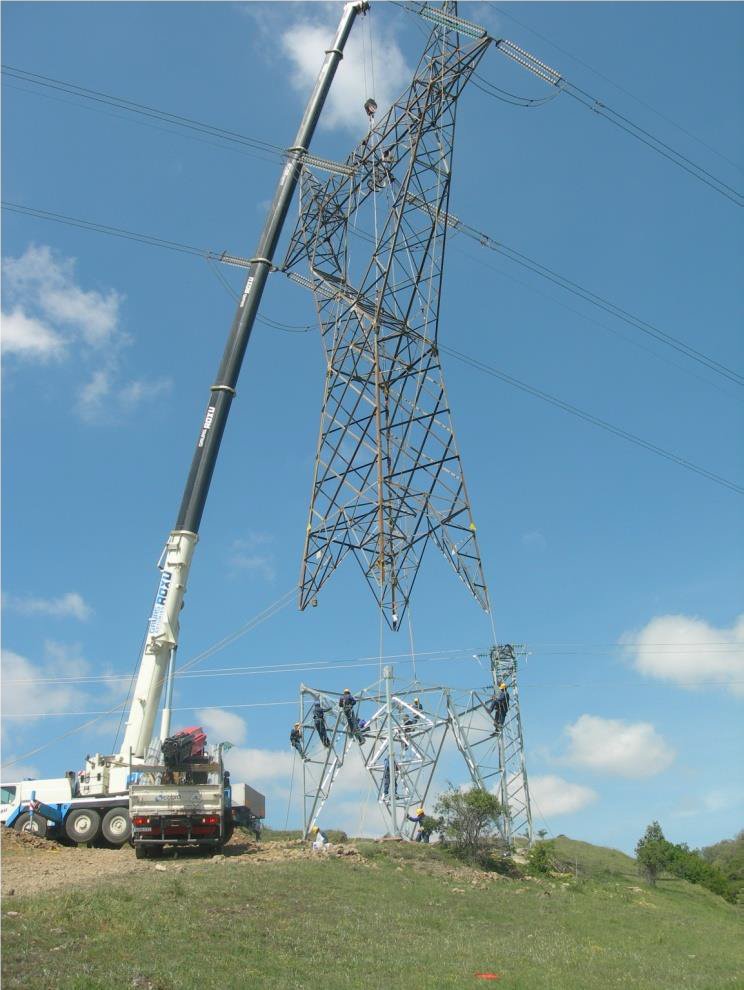

Tower lifting by crane to allow clearances for reconductoring
Types of high-temperature conductors are commercially available since many years. They are made of different materials, including composite cores. In the last years, more sophisticated acceptance tests have been proposed and certain installation problems have been identified. Sag-tension calculations at high temperature, AC resistance, internal conductor temperature variation, and heat transfer at very high temperatures has been reviewed and updated.
Reference Paper RP_307_1 Overhead Transmission Lines, Gas Insulated Lines and Underground Cables
This Reference Paper is a work of the three SCs B1, B2 and B3, where B1 had the lead. It refers to transmission lines exceeding 170kV alternating current (AC). Direct current (DC) connections and subsea cables are not a part of the scope of this paper (for those, other criteria apply to compare).

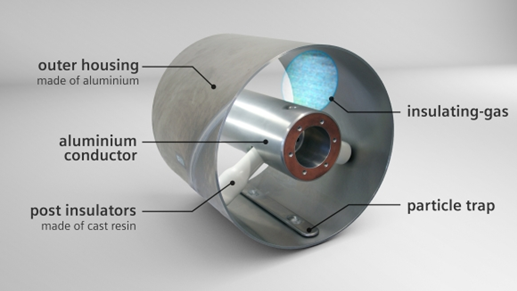

There is a considerable amount of highly technical information, specifications and guides available on the transmission of bulk electrical power from one area to another. This information is available from bodies such as CIGRE, IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), and many National-based organizations. There is, however, very little information that would explain the fundamentals of the technologies in such a manner that it could be understood by a non-technical person or a person not involved on a day-to-day basis in that industry. This paper will attempt to fulfil that need by providing basic information in hopefully a readily understandable manner.
CIGRE “Science and Engineering” published two articles with relevance for SC B2:
- CSE 13: Comparative study of the long-term reliability of HTLS conductor systems
- CSE 14: Wire Displacement of AAAC Overhead Line Conductors at Wedge Tension Clamp
The following publications are expected in 2020:
- TB 788 Dynamic Load Effects on Overhead Lines- Impact on Foundations has been published January 2020
- WG B2.24 Qualification of HV and UHV Overhead Line Supports Under Static and Dynamic Loads
- WG B2.40 Calculations of the electrical distances between live parts and obstacles for OHL: Preparatory studies for revision of IEC standard (IEC61865 –IEC60826 –EN50341)
- WG B2.61 Transmission Line Structures with Fibre Reinforced Polymer FRP Composites
- WG B2.62 Compact HVDC overhead lines
- WG B2.63 Compact AC lines
Tutorials in 2019
Montreal, Canada, September 2019, CIGRE Canada Conference
- Tutorial on TB 695 (Experience with the mechanical performance of non-conventional conductors)
- Tutorial on TB 631 (Coatings for protecting overhead power network equipment in Winter conditions)
Delhi, India, November 2019, CIGRE SC A2, B2, D1, Colloquium
- Tutorial on TB 695 (Experience with the mechanical performance of non-conventional conductors)
- Tutorial WG B2.61 (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composite Structures for Electrical Transmission Lines)
- Tutorial on B2.TF007 (Interaction of surge arresters and vibration dampers), SC B2 Technical meeting, Colloquium New Delhi, India, November 2019
Sao Paulo, Brazil, October 2019, XV SIPDA Conference (International Symposium on Lightning Protection)
- Tutorial on TB 694 (Ground potential rise at overhead AC transmission line structures during power frequency faults)
Aalborg, Denmark, June 2019, CIGRE Symposium “Going offshore“
- Tutorial on TB 583 (Guide to the conversion of existing AC lines to DC operation).
Customer Advisory Group (CAG)
CAG decides about future Working Groups, based on suggestions for new works and based on the needs of the customer target groups.
The Target Groups of SC B2 are especially: Executives, Consumers, Regulators, Energy Traders, Equipment Suppliers, Consultants, Maintenance Groups, Asset Owners, Asset / Facility Managers, Governments, Authorities, Power System operator, Distributors, Grid Planners, Public, Media, Universities, Research Institutes, Schools, International Organizations: e.g. CIRED, IEEE, IEC, CENELEC, ASCE
The following topics are discussed for new WGs in the near future:
- Use of High Temperature Low Sag (HTLS) Conductors in New Overhead Line Design
- Foundations for Difficult Soil and Geological Conditions
- Mitigation of electrically induced audible noise from overhead lines AC and DC
- Risk Management of Overhead Line networks: A model for identification, evaluation and mitigation of operational risks
- Enhancing Overhead Line Rating Prediction by Improving Weather Parameters Measurements
- Numerical Simulation of electrical fields on AC and DC Overhead Line Insulator Strings
- Increasing the Strength Capacity of Existing Overhead Transmission Line Structures
- Guide for Design, Construction and Installation of Emergency Restoration Systems to Use in Repair/Maintenance Operations of Overhead Lines
Participation to Regional Meetings, Colloquia and Symposia
- 2019 April, Hakodate (Japan) CIGRE IEC UHV/EHV Colloquium
- 2019 May, Iguaçu (Brazil) XVIII RIAC – Iberian American Regional Meeting of CIGRE
- 2019 June, Aalborg (Denmark) Symposium B1, B2, B4, C1, C2, C4 “Going offshore – challenges of the future power super grid”
- 2019 September, Montreal (Canada), CIGRE Canada Conference
- 2019 November, New Delhi (India) International Joint Colloquium A2, B2, D1, and SC B2 annual meeting
- 2019 November, Belo Horizonte (Brazil) SNPTEE – Brazilian Seminar on Production and Transmission of Electric Energy

