Energy Sectors Integration and impact on power grids
Energy Sectors Integration (ESI) denotes the system that coordinates the generation, transmission, conversion, and utilization of energy across different energy sectors, pathways, and time scales. Compared with “classical” energy system in which energy sectors are treated independently, ESI has four main advantages: 1) accommodating higher penetration of renewable energy using the flexibility from energy conversion and energy storage; 2) increasing the efficiency of the whole system by cascade utilization of energy including renewable energy; 3) promoting the optimal deployment of both centralized and decentralized energy resources at a system level through market interaction; and 4) enhancing the reliability and resilience of energy supply through the complementation of different energy infrastructures. The couplings and interactions among multiple energy networks, for example, power, gas, hydrogen, heat/cooling networks, as well as electro mobility, are becoming more and more complex. For example, there are increasing concerns on the coupling of the gas market and power market in US and Europe.

by Ning Zhang, WG C1.47 Convenor, and Antonio Iliceto, SC C1 Chair
ESI can be categorized into two levels, that is, local level energy systems and multi-region level energy networks. The local level energy systems mainly focus on the energy coupling in distribution or consumer level (e.g., school, hospital, or a community). It includes electricity distribution systems, gas distribution stations, gas pipes, heat exchange stations, and district heat networks. The multi-region level energy networks mainly denote the energy transmission networks connecting source side and demand side, including long-distance power, gas, hydrogen transmission networks. These networks usually do not have a large scale, but their operation also has an impact on the planning and operation of other systems. The management of large scale water resources/river basins to cater for both electricity and water supply show the need of an effective and inclusive sector coupling. Indeed, with the increasing trend of energy sector coupling, the challenges and opportunities should be investigated from the infrastructure planning and operational optimization points of view.
There have been two Working Groups (WGs) on energy system coupling in CIGRE. JWG C6/C2.34 examines drivers and requirements for flexibility as well as flexibility contributions from distributed energy resources. JWG C6/C1.33 studies the configurations, impacts and prospects of multi-energy systems from demand and distribution side. To further promote the development of ESI, more work should be done from the perspective of transmission network. To this end, CIGRE has set up a new WG C1.47 titled Energy Sectors Integration and impact on power grids to investigate the current progress in energy sector coupling at transmission grid level. The Terms of Reference for the Working Group were approved in September 2020.
Working Group aim and scope
The aim of this WG is to address the technical, business, economic and regulatory issues for the developing of concrete use cases of energy systems coupling and assess state-of-the-art research in different countries around the world. The Working Group will also bridge the gap between academy research and industry on the ESI to reveal the key issues that should be addressed in the future.
The scope of this WG is to:
- Identify technical / business / institutional challenges and benefits from energy sector integration at transmission grids level.
- Review the methodology and technologies on the modeling, operation, market analysis and planning towards multi-region level ESI.
- Summarize lessons learned and introducing best practice of energy sector integration.
- Propose suggestions for policies and market regulations towards the energy sector integration at transmission grids level.
- Promote technical papers, technical panel sessions, and workshops for the dissemination of academic research and real-world applications of energy sector integration.
- Coordinate such activities where appropriate with other CIGRE committees, subcommittees, and Working Groups.
For the above topics, a survey of state-of-the-art, technical advances and typical cases will be done, analyzing the drivers and solutions for the selected planning and operation towards energy sectors coupling at transmission level, with scope to infer some general principles as useful guidelines for the design of future integrated multi-energy systems.
Difference with the existing Working Groups
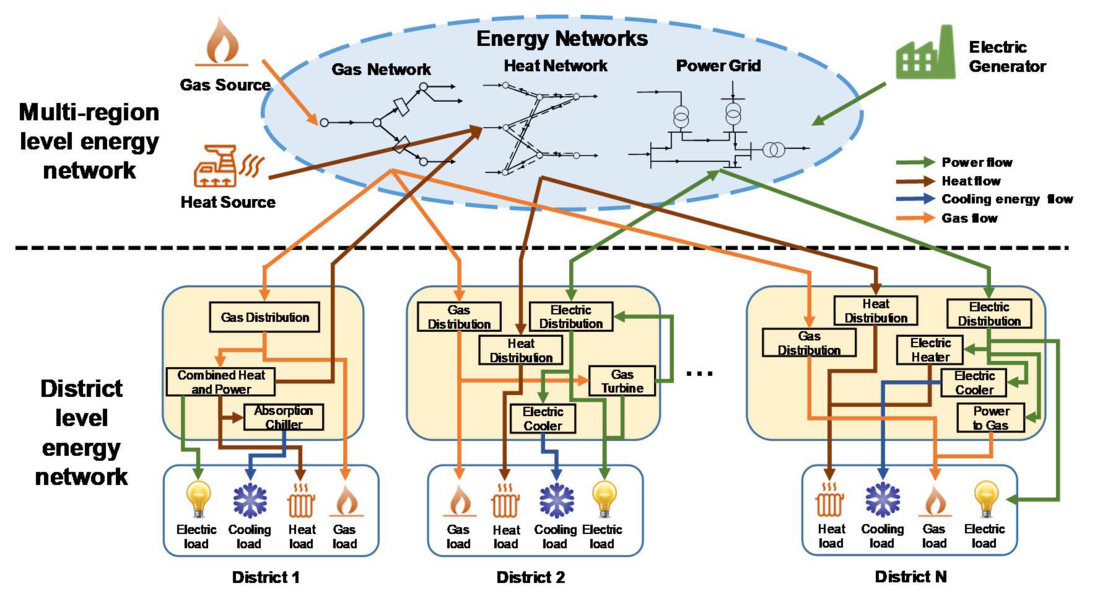
Figure 1 - District level energy networks and multi-region level energy networks
The existing two CIGRE WGs are focused on ESI in distribution network (i.e. the district level energy networks in Fig.1), while this WG is focus on the ESI in transmission network (i.e. the multi-region level energy networks in Fig.1). There are some significant differences between these two categories of ESI:
- The energy transmission characteristics are usually omitted in district level energy networks, while the transmission network analysis is one of the main focuses in the multi-region level energy networks. That is, besides the steady-state models, the dynamic models of heat and gas networks should be considered in the modeling of multi-region level energy networks because their transient state processes cannot be ignored in operation optimization.
- For the district level multi-energy system in each region, the physical distances between the energy converters and storage devices are relatively short (e.g., the combined heat and power unit and heat storage device may be built in the same building) and can hardly have congestions. In addition, the construction locations of these devices and the parameters of lines/pipelines between them are also difficult to obtain at the planning stage. Therefore, the transmission characteristics of the lines or pipelines can be neglected in the district level multi-energy system, and energy hub model is a good choice for district level multi-energy system modeling. For the long-distance energy networks connecting regions, the detailed network constraints should be considered.
Work plan
Regular WG meetings will be held online. The physical Working Group meeting is planned to be held in Q3/2021 & 2022 in Paris General Sessions. Questionnaires will be designed and distributed in Q4/2020, and the collection of survey results will be finished in Q2/2021. In Q3/2021, the collected data will be compiled and analysed. The best practice of sectors coupling will be chosen in Q4/2021. The draft report is planned to be finished by Q1/2022. The milestone report to C1 will be finished by Q2/2022. Finally, the WG is planning to complete its analysis and to document the results in the Technical Brochure scheduled for October 2022.
Thumbnail credit: Alina Grubnyak on Unsplash



