Power system technical performance
By Zia Emin, Chair & Genevieve Lietz, Secretary
Overview of Study Committee C4
Study Committee (SC) C4’s main mission is to facilitate and promote the progress of power systems engineering and the international exchange of information and knowledge in the field of system technical performance and to add value to this information and knowledge by means of gathering state-of-the-art practices from around the world and developing recommendations. The main approach is through the formation of working groups (WGs) and the publication of CIGRE Technical Brochures; some recent examples are provided at the end of this brief report. The other approach is through sponsoring and promoting colloquia around the world which focus on the key technical challenges in modern power systems that relate to system technical performance.
The scope of SC C4 is the development and review of methods and tools for analysis related to power systems, with particular reference to dynamic and transient conditions and to the interaction between the power system and each of the following: (i) its apparatus/sub-systems; (ii) external causes of stress; and (iii) other installations. Specific issues related to the design and manufacturing of components and apparatus are not within the scope of SC C4, nor are those specifically related to planning, operation and control, apart from cases in which a component, apparatus, or subsystem behaviour depends on, or significantly interacts with, the performance of the nearby power system.
The SC C4 scope covers system technical performance phenomena that range from nanoseconds to hours, which includes everything from lightning, switching, power quality, electromagnetic compatibility and electromagnetic interference (EMC/EMI) and insulation coordination to power system stability, modelling and long-term system dynamics.
As the scope is quite broad and covers all aspects of the technical performance of large power systems, further work was carried out to better explain the timeframe of various phenomena. This work is nearing its completion and the timeframes of various phenomena are given in Figure 1. The output of this work will be included as an appendix in the SC C4 strategic plan.
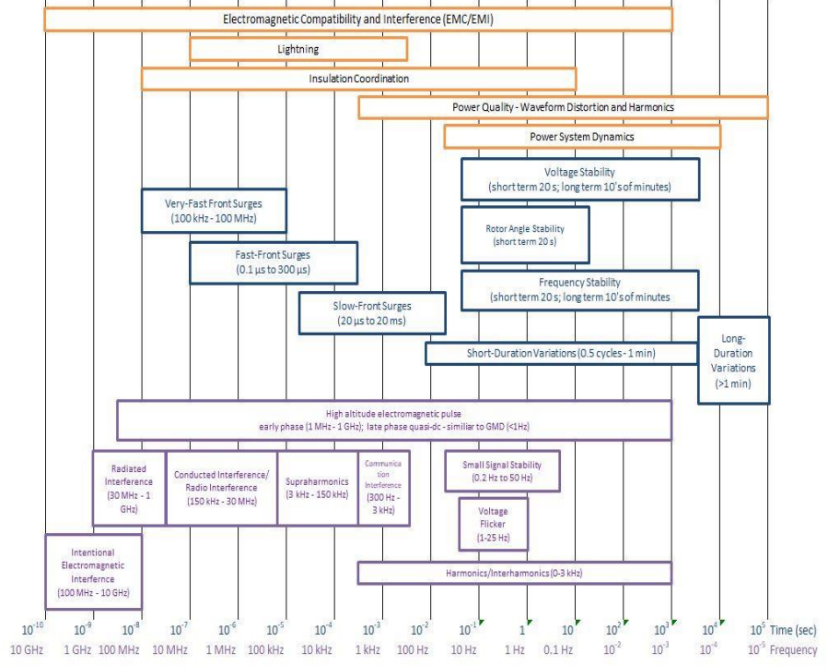
Figure 1 - Range of phenomena investigated by SC C4
Due to its wide remit, SC C4 alone cannot investigate power system technical performance issues without a solid understanding of the equipment itself, its performance, system planning and operational issues and environmental factors that may play a role in system performance. This leads to close cooperation between SC C4 and other CIGRE SCs that deal with equipment, system planning and operations, distribution networks, materials and testing, and environmental aspects of the power system. The close cooperation can be seen from the establishment of several Joint Working Groups (JWGs). Furthermore, nomination and establishment of liaison members from other SCs in SC C4’s WGs and vice versa also adds to the close collaboration between SC C4 and other SCs. At the time of writing, there are 12 JWGs with SCs A1, A2, A3, B1, B2, B4, B5, C1 and C2. Furthermore, two SC C4 WGs are joint with CIRED on issues related to distribution networks. There are also two JWGs between SC C2 and IEEE owing to the increasing cooperation between the two organisations. SC C4 also has formal liaisons with the IEC TC 77 (on EMC) and the International Special Committee on Radio Interference (CISPR).
SC C4 Structure and Strategic Direction
SC C4 is composed of 24 regular members, 3 additional regular members and 18 observer members, together with a chairman and a secretary representing 42 countries. SC C4 presently consists of some 39 WGs performing highly technical work aligned with the strategic fields of SC C4. These WGs are composed of over six hundred individual technical experts from 50+ countries around the world, some serving in more than one WG.
There are also three Advisory Groups (AGs) within SC C4. AG C4.1 is a group of experts that consults on the strategic directions for SC C4 and it includes liaisons with IEC and IEEE. AG C4.2 on Customers reviews and prioritises the composition of target groups and identifies improvements and opportunities for communication of the SC target groups. AG C4.3 on Tutorials and Conferences coordinates SC C4’s activities with respect to colloquia and tutorials.
The SC C4 annual meeting in 2021 took place online during the Virtual Centennial Session week and some of the participants (SC Regular Members, AG members and WG conveners) are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 - Some of the participants (41 out of 55 individuals present) from the 2021 online meeting of SC C4.
Main technical areas of activity in SC C4
Below is a brief summary of WG activities in the main technical directions within SC C4. A complete list of all active SC C4 WGs with their annual reports is available on the SC C4 KMS space.
Power Quality
Currently there are six WGs concentrating on power quality related issues of present and future power systems. Work in most of the WGs is at an advanced stage. The WG C4.42 is looking at the important issue of low-order harmonic emissions from loads considering the changing load characteristics due to an increasing penetration of power electronic based loads and it is approaching completion. The work of WG C4.40 is closely related and equally important in this area as it is trying to revise the relevant IEC Technical Reports, i.e. IEC 61000-3-6, 61000-3-7, 61000-3-13 and 61000-3-14. WG C4.49 is looking at multi-frequency instabilities of grid-tied converter based modern power systems crossing both stability and power quality analysis areas; and WG C4.51 is addressing traction supply points and the impact these points may have on the wider system with respect to power quality.
The two new WGs created in this technical direction are WG C4.63 looking at harmonic power quality standards and approaches from a comparative viewpoint, and WG C4.65 which is addressing the specification, validation and application of harmonic models for inverter-based resources. Both WGs are at the beginning stages of their work.
Electromagnetic Compatibility and Electromagnetic Interference (EMC/EMI)
Electromagnetic Compatibility and Electromagnetic Interference (EMC/EMI) issues addressed by SC C4 cover emission and immunity problems resulting from disturbances that are not addressed under the subject of power quality. These include disturbances produced by the electrical power system as well as disturbances of external origin able to interfere with the electrical power system. Such disturbances can affect the integrated system performance by electrical conduction (electrical contact), induction (electric or magnetic fields) or radiation (high-frequency electromagnetic field). Health effects related to low-frequency electromagnetic field (EMF) are excluded, whilst intentional electromagnetic interference (IEMI) is instead included.
There are four active WGs within SC C4 that can be classified as being related to EMC. WG C4.44 is focusing on EMC for large photovoltaic systems and its work is at an advanced stage. Two further WGs include WG C4.54, which is looking at the protection of HV power network control electronics from the high-altitude electromagnetic pulse (HEMP), and WG C4.55, which is examining EMC related very-fast transients in gas-insulated substations. A recently formed WG, C4.68, will work on identifying EMC issues in modern and future power systems building on the work that was achieved a few years ago by the now disbanded WG C4.24.
Insulation Coordination
There are six active WGs within the technical direction of insulation coordination. Two WGs concentrate on overvoltage related issues: JWG B4/B1/C4.73 on the surge and extended overvoltage testing of HVDC cable systems with a goal to produce recommendations on methods for determining lightning levels in mixed OHL-cable systems; and WG C4.46 on the evaluation of temporary overvoltages. WG C4.48 on the other hand is trying to formulate overvoltage withstand characteristics of power system equipment from 35 to 1200kV. These are complemented by JWG B1/C4.69, which is specifically addressing the development of insulation coordination recommendations on AC cable systems. Two well-advanced WGs include WG C4.50, which is investigating the evaluation of transient performance of grounding systems in substations, and JWG C4/A3.53, which is looking at the application of advanced metal-oxide varistors for surge arresters with better protection properties. There are a few WGs that are under consideration in a similar technical direction.
Lightning
Lightning is one of the most important natural phenomena that impacts and interacts with the electric power network necessitating advanced knowledge of lighting current parameters. There are presently nine WGs investigating various aspects of lightning. WGs C4.36 and C4.39 (at the completion stage) are looking at lightning parameters and engineering consequences for wind turbines and effectiveness of line surge arresters for lightning protection of OHLs respectively; both WGs are nearing completion. WG C4.43 is well advanced in its work reviewing lightning protection design schemes for structures from the viewpoint of avoiding physical damage and overvoltages that could generate flashover at electric apparatus and lines, and investigating the applicability of these schemes to nuclear power plants. Two other WGs include WG C4.57, which is looking specifically at formulating guidelines for the estimation of lightning performance of distribution lines; and JWG B2/C4.76, which is concentrating on lightning and grounding considerations during rebuilding or refurbishment of overhead lines for both AC and DC. WG C4.59 is addressing real-time lightning protection in relation to the networks of the future where digitisation is heavily in use. There are three further WGs that were formed very recently: WG C4.61 investigating lightning transient sensing and monitoring, WG C4.66 researching new concepts for analysis of multiphase back-flashover phenomena, and WG C4.67 investigating the lightning protection of hybrid overhead lines.
Power Systems Dynamic Performance Models and Numerical Analysis
The subject of system dynamics and the overall system performance in terms of various stability parameters is gaining significant attention in the face of increased connection of power electronic based devices. This trend is obvious from the number of WGs within this technical direction with a total of fourteen WGs looking at many important issues of present and future concerns for power system dynamics and analysis. These include subjects such as:
- Impact of Low Inertia Network on Protection and Control (JWG B5/C4.61)
- Guidelines for Sub-synchronous Oscillation Studies in Power Electronics Dominated Power Systems (JWG C4/B4.52)
- Electromagnetic Transient Simulation Models for Large-Scale System Impact Studies in Power Systems having a High Penetration of Inverter Connected Generation (WG C4.56)
- Evaluation of Voltage Stability Assessment Methodologies in Transmission Systems (JWG C4/C2.58/IEEE)
- Generic EMT-Type Modelling of Inverter-Based Resources for Long Term Planning Studies (WG C4.60)
- Review of Phasor Measurement Unit Applications (JWG C4/C2.62/IEEE)
- Application of Real-Time Digital Simulation in Power Systems (WG C4.64)
These WGs, and several others that are at a more advanced stage, are investigating challenging technical issues associated with modelling, simulation and dynamic performance assessment of power systems around the world. The ever-increasing penetration of renewable energy sources as part of the generation mix is driving the formation of more WGs in this area due to the need to understand the level of technical performance issues facing the grid of the future.
Newly formed Working Groups
Ten new WGs have been established since October 2020:
- WG C4.60: Generic EMT-Type Modelling of Inverter-Based Resources for Long Term Planning Studies
- WG C4. 61: Lightning transient sensing, monitoring and application in power systems
- JWG C4/C2.62/IEEE: Review of Phasor Measurement Unit Applications
- WG C4.63: Harmonic power quality standards and compliance verification
- WG C4.64: Application of Real-Time Digital Simulation in Power Systems
- WG C4.65: Specification, Validation and Application of Harmonic Models of Inverter Based Resources
- WG C4.66: New concept for analysis of multiphase back-flashover phenomena of transmission lines due to lightning
- WG C4.67: Lightning Protection of Hybrid Overhead Lines
- WG C4.68: EMC issues in modern and future power systems
- JWG C1/C4.46: Optimising power system resilience in future grid design
SC C4 has traditionally established around 5-6 new WGs per annum over the past several years. However, the number of the existing WGs completing their mandate has been delayed due to current pandemic-related effects and hence the impetus to form new WGs was affected back in 2020. During the 2020 annual SAG and SC meetings, it was decided to put together a list of areas that require further consideration and propose possible new WGs. The WGs in SC C4 listed above were formed as a result of this gap analysis and work is in progress to propose further WGs.

CIGRE active Working Groups / Call for experts
Publications
Technical Brochures
The following Technical Brochures have been published since October 2020 as a result of work done by SC C4 WGs and JWGs:
At least two further Technical Brochures are expected to be finalised and submitted for publication before the end of 2021:
- JWG C2/C4.41 “Impact of high penetration of inverter-based generation on system inertia of networks”; and
- WG C4.39 “Effectiveness of line surge arresters for lightning protection of overhead transmission lines”.

Reference Papers
SC C4 has produced one Reference Paper since October 2020:
The Reference Paper had an accompanying paper published in the CIGRE Science & Engineering journal.
Green Books
SC C4 embarked on a new Green Book on “Power system dynamic modelling and analysis in evolving networks” to be co-edited by Dr Babak Badrzadeh and Dr Zia Emin. Various chapters within the book will be led by SC C4 experts. The Green Book on power system dynamic modelling and analysis will provide information about all aspects of contemporary power system dynamic modelling and analysis in a rapidly changing power system with increasing uptake of inverter-based resources. It will also provide a comparison of changes occurring in conventional power systems with a dominance of synchronous generators, and an evolving power system with a high share of grid-connected and distributed inverter-based resources. Topics that will be addressed include dynamic phenomena experienced, analysis methods and simulation tools required, and enablers to achieve this.
Tutorials and Conferences
Since October 2020, SC C4 has supported the following events:
- CIGRE 2021 Virtual Centennial Session (VCS) which replaced the 2021 Centennial Session. As part of the VCS Session, SC C4 had two General Discussion Meeting sessions. Both of these were half-day events run via the Paris studios by the SC Chair and Professor Claus Leth Bak (DK). SC C4 also ran a tutorial and a workshop (see Figure 3).
- The General Discussion Sessions were moderated by Special Reporters Dr David Jacobson (CA) and Professor Filipe Faria da Silva (DK) who were supported by Ms Marta Val Escudero (IE);
- The tutorial entitled “Challenges with series compensation applications; the case of overcompensated lines” was based on the work done by JWG C4/B5.41 and was presented by Dr Liisa Haarla (FI), Krish Narendra (CA) and Sachin Srivastava (IN); and
- The Workshop on “EMT analysis for large-scale system impact studies in power systems having a high penetration of inverter connected generation” was organised by Dr Babak Badrzadeh (AUS) with presenters from a few different sectors and countries.
All individuals who supported SC C4 VCS efforts are shown in Figure 4.

Figure 3 - SC C4 Virtual Centennial Session events

Figure 4 - Individuals that supported SC C4 at the 2021 Virtual Centennial Session
In terms of upcoming events supported by SC C4, the next major event will by the Kyoto Symposium in April 2022 followed the Paris 2022 Session.
In addition, the following webinars were delivered in 2021; the last three in conjunction with the National Committee in India:
- WG C4.23: Procedures for Estimating the Lightning Performance of Transmission Lines – New Aspects, by C.S. Engelbrecht, F.H. Silveira, I. Tannemaat and S. Visacro (July 2021).
- WG C4.28: Extrapolation of Measured Values of Power Frequency Magnetic Fields in the Vicinity of Power Links, by P. Munhoz (March 2021).
- JWG C4/C6.35/CIRED: Modelling and Dynamic Performance of Inverter Based Generation in Power System Transmission and Distribution Studies, by K. Yamashita, H. Renner, S. Martinez and P. Aristidou (February 2021).
- WG C4.31: Assessment of Conducted Disturbances above 2 kHz in MV and LV Power Systems, by D. Thomas (February 2021).
Awards
The following individuals associated with SC C4 work in the past or currently (some members work across SCs) were recognised with various CIGRE awards:
- David Jacobson (CA): Technical Council award;
- Liisa Haarla (FI) and Marta Val Escudero (IE): Women in Energy (WiE) award;
- David Jacobson (CA), Filipe Faria de Silva (DK), Marta Val Escudero (IE), Genevieve Lietz (DE), Babak Badrzadeh (AUS) and Andrew Halley (AUS): CIGRE Pioneer e-session achievement award.

Figure 5 - SC C4 TC and WiE award recipients David Jacobson, Marta Val Escudero and Liisa Haarla


