Survey on the current state of telecommunications in power utilities
In 2020, CIGRE Study Committee D2 issued a Telecommunications survey to CIGRE member countries. The purpose of this survey was to obtain the current technological state of the member countries' use of telecommunications technologies in power utility specific applications.
By Victor Tan (AU) (Convenor); Jaume Darne (ES) (Editor); Zwelandile Mbebe (ZA) (Editor); Louise Watts (AU) (Editor); Marcelo Costa de Araujo (BR); Karen McGeough (IE), Jasmina Mandic Lukic (CS), Mehrdad Mesbah (FR)
Acronym | Definition |
|---|---|
3G | Third Generation Cellular |
4G | Fourth Generation Cellular |
IP | Internet Protocol |
LTE | Long Term Evolution |
MPLS | Multi-protocol Label Switching |
MPLS-TP | MPLS Transport Profile |
PDH | Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy |
PMU | Phasor Measurement Unit |
SCADA | Supervisory control and data acquisition |
SDH | Synchronous Digital Hierarchy |
TDM | Time Domain Multiplexing |
VHF | Very High Frequency |
From the responses, it was found that many utilities have a mix of technologies co-existing in their telecommunications networks.
The following provides a summary of the major service types in power utilities' telecommunications networks, and the transports technologies used to carry these services:
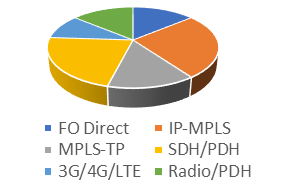
SCADA
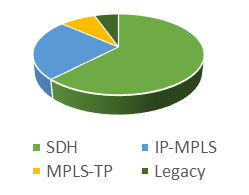
A variety of telecommunications technologies are used to carry this service. These technologies range from the legacy TDM-based technologies to the newer packet-based technologies. The survey results show that around 62% of the respondent utilities carry SCADA over SDH, followed by IP-MPLS (24% of respondents), MPLS-TP (8%) and legacy technologies such as VHF radio or Serial Channels over Pilot wires (5%).
Differential Protection
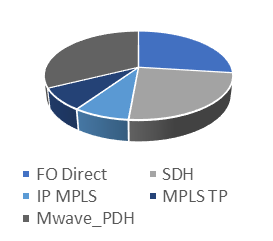
Non-packet technologies are primarily used to carry this service in the survey participants' networks. However, several respondents have reported using packet-based technologies to carry differential protection. The survey results show that around 32% of respondents use legacy telecommunications technologies (PDH) to carry this service, followed by direct fibre optical connections (27%) and SDH (24.5%). For the packet-based technologies, IP-MPLS and MPLS-TP form a combined 16% of use cases.
Distance Protection
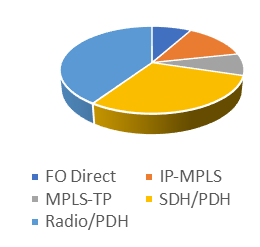
This is the most widely used protection method and it was expected that a mix of technologies would be used to carry this service. The results have shown that PDH technology is predominately used by utilities to deliver this service, with 40.5% over Radio and 30% over SDH. This service is carried by other technologies in the following order: IP-MPLS (13.5%) MPLS-TP (8%) and dedicated optical fibre pair (8%).
Phasor Measurement Unit (PMU)
PMU transport is carried largely by the following technologies: SDH (22%), IP-MPLS (22%), Microwave Link (20%), dedicated Optical Fibre pair (14.5%), MPLS-TP (5%) and Pilot Wire (5%).
It is interesting to note that 12% of the respondents are not currently using PMUs and have no plans to deploy PMUs.
Other Services
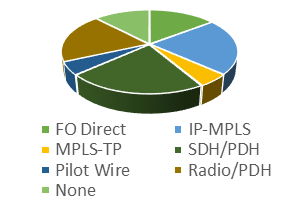
"Other services" include operational telephony, video surveillance and other services not explicitly listed in the results. There are a range of transport technologies used to deliver these services, with IP-MPLS in 26% of the cases, followed by the SDH in 22%, and direct optical fibre, MPLS-TP, and point-to-point radio links in 14%. Additionally, cellular technology 3G/4G/LTE is used by 10% of the respondents.
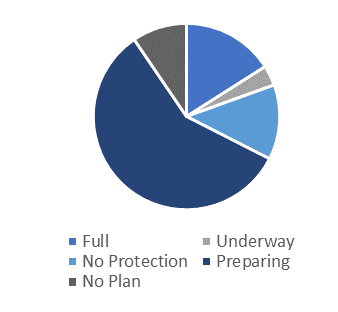
Another purpose of this survey was to obtain an overview of the utilities' plans in their telecommunications networks. A common theme from the responses was the focus on modernisation of the telecommunications network. Most respondents have started to migrate from the traditional circuit switched networks to packet-based networks. The survey results show that:
- 16% of the respondents have fully migrated their network to a packet-based-only network,
- 3.5% have plans to migrate to a packet-based-only network,
- 13% are planning to migrate all services to a packet-based network, excluding protection services - this implies that a non-packet-based network is retained or operated in parallel,
- 58% of the respondents have started migrating non-protection services, including data, SCADA, and telephony services over packet-switched networks; and,
- 9.5% of respondents have no migration plans.
From the results of the survey, it was found that a majority of the respondents plan to migrate their legacy TDM-based networks such as PDH or SDH, to a packet-based telecommunications network. This came as no surprise to us, due to the need to address obsolescence of their existing legacy TDM-based telecommunications equipment. Most respondents also see this as an opportunity to improve the operational efficiencies and new possibilities that packet-based technologies bring, and to reduce the long-term costs in supporting current generation technologies through their adoption of packet-based networks.
This survey provided a high-level overview of the current state and the migration plans of telecommunications technologies among Cigre member utilities. Telecommunications is a wide-ranging and complex topic which covers many adjacent areas of interest such as cyber security and power system protection. We have found it to be impractical to attempt to cover too much ground in a single survey, which often result in too many questions with a loss of focus. Follow up surveys would be appropriate in the future, to delve deeper into specific questions, for example, on cyber security network topics, and wireless technologies. This survey had 63 responses from Cigre member countries with the major representations from Asia, Oceania, Eastern Europe and Africa. An improvement in future surveys is to include more responses from other geographical areas to provide more balanced worldwide responses.
Thumbnail credit: adamkaz on iStock

