Life Extension of Oil filled Transformers and Shunt Reactors
Considering Transformer Life Extension? Answer These Questions First.
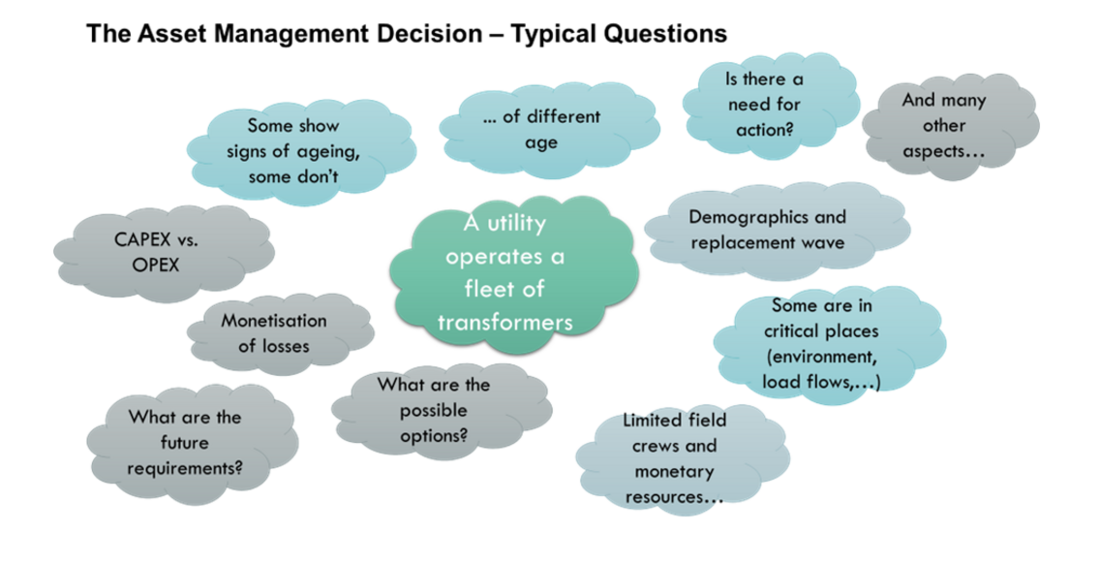
When asset managers need to consider measures to extend the life of transformers, typical questions have to be answered and evaluated. This is necessary on the one hand, to comply with the corporate strategy and on the other hand, to be able to document and justify decisions accordingly.
Members
Convenor
(CH)
P. MULLER
Secretary
(CH)
R. SCHNEIDER
M. ANGLHUBER (AT), R. ASANO (BR), A. AZNAR BLANES (ES), A. BAJWA (GB), B. BOURGEOIS (FR), S. CHEN (FR), K. DIOKA (ZA), J. EMMEL (CH), E. FIGUEROA (CA), S. FLOOD (IE), M. FOATA (DE), N. GUSTAVSSON (SE), P. GUY (AU) K. HECHT (CH), W. HUSKA (AT), R. IGNACIO (BR), A. ILGEVICIUS (DE), S. JAUFER (CH), M. KADOWAKI (JP), M. KRUEGER (AT), J. KRUSE (DK), I. KUDELA (PL), R. KUTZNER (DE), D. KWEON (KR), J. LUKIC (RS), A. MJELVE (NO), M. MONCEAUX (CA), A. SBRAVATI (US), A. SHKOLNIK (IL), M. SUSILLA FERNÁNDEZ (ES), C. VILA (ES), D. WALKER (GB), P. WARCZYNSKI (PL), S. ZHANG (CN)
Introduction and Objectives
During the last decades, a strategy change from time-based to condition-based and risk-based maintenance has been observed. In this context, asset managers are permanently looking to optimise equipment usage. As transformer diagnostic techniques improved in recent years, operators have been looking for techniques, measures, and methods to extend the life span of installed transformers and reactors. This brochure should be considered as a guideline for approaching transformer life extension projects.
Structure and Content of the Technical Brochure
The introduction focuses on the terms of reference and gives the reader an overview of existing CIGRE brochures related to life extension topics. Furthermore, the remnant life of a transformer or reactor is discussed, and clear definitions are given regarding different end of life scenarios and lifetime extension measures. The first chapter closes with a typical set of questions an asset manager could have when facing a transformer life extension project. The content of the brochure should enable the reader to answer relevant questions and refers to other documents handling specific topics cited in the appendix.
The second chapter deals with the decision-making process and the related strategy, a topic which should be tackled prior to the initiation of a life extension project. It shows the major topics to be considered for developing an asset management strategy. These include regulation, financial rules and the economic analysis with life cycle costs and net present value (NPV) consideration. Furthermore, focus is given on the costs of losses, failures, and unplanned outages. At the end of the chapter, an approach is shown to assess the criticality of non-quantifiable costs linked to environment, safety, and network availability.
The third chapter provides an overview of the transformer and reactor main parts such as active part including solid and liquid insulation, bushings, tank and cooler, tap-changer. It covers their aging mechanisms as well as the consequences regarding the lifespan of the equipment. The change in properties of insulating materials due to ageing, the solid insulation dimensional change by mechanical stress and moisture, the risks of moisture, the property change of liquid insulation as well as contact ageing are discussed. As knowledge about the condition of transformers and reactors is important for the selection of adequate measures to apply, the chapter gives an overview regarding analysis tools and methods for the detection of common failures and degradation. Finally, a flowchart shows how to come from an observation to a diagnosis.
Considering the condition of the equipment, life extension methods have to be evaluated regarding their applicability and efficiency. The fourth chapter gives a detailed technical description of existing solutions to improve the life span of relevant transformer components. The focus is given on major interventions like oil treatment, drying, sealing and rust treatment, additionally replacement or upgrade of components including bushings, tap-changers, etc. At the end, an example of a complete refurbishment of a generator step-up transformer including active part exchange is presented.
In order to determine whether a life extension intervention is economically reasonable, a business case must be created. The objective of chapter five is to show how such business cases can be structured by providing a basic methodology to asset managers. The financial benefits and proper timing of an intervention is considered, and a net present value (NPV) analysis is performed for different scenarios. Examples are given for cellulose insulation drying, sealing an oil preservation system, enhancing transformer cooling, increasing reliability through replacement or refurbishment of components and mid-life refurbishment.
Appendix A covers the surveys performed by the working group about method and best practice of life extension measures.
Appendix B gives substantially more information related to each single diagnostic tool mentioned in chapter three including references.
Furthermore, the Appendix C shows nine case studies of utilities performing life extension projects.
Conclusions
In some circumstances, it may be debatable whether a performed intervention can be considered a life extension. In order to have a clear view the following definition has been applied to this Technical Brochure.
Life extension is defined as a set of major interventions on a transformer, beyond “normal” maintenance and repair, to remedy its problems, restore its condition and postpone a predicted end of functional, economic, or reliable life. It is applicable but not limited to aged transformers with or without defects or faults, functional or failed.
Figure 1 shows how life extension measures, as considered by the brochure, will fit into the maintenance process (adapted from Technical Brochure 445 “Guide for Transformer Maintenance”).
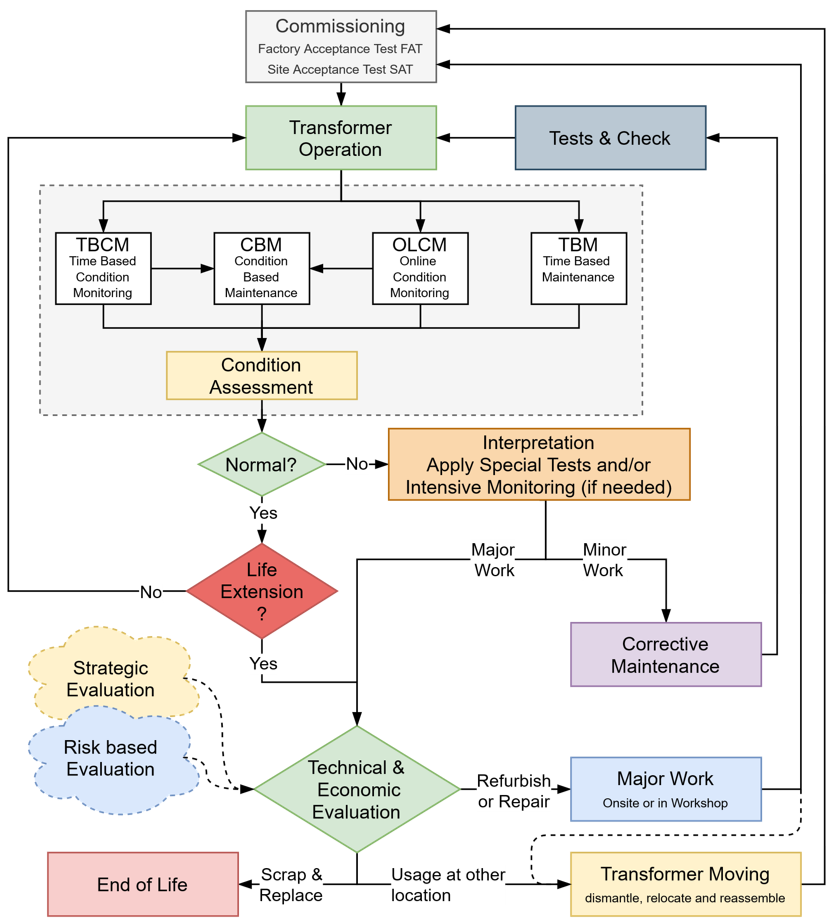
Figure 1 - Life extension measures in the maintenance process
There are important questions that are typically almost always asked by the person in charge of proposed life extension measures and are related to:
- Fleet management strategies
- Financial and regulatory considerations
- Screening for possible candidates for life extension
- Methods and good practice of life extension
- Decision making - business case of life extension.
So, the question now is: How does this brochure enable the reader to answer the typical questions related to these topics?
Fleet Management Strategies
The brochure shows an approach to adding life extension as an alternative to the classic existing “repair or replace” strategy. By implementing life extension as an alternative, the replacement wave of an aging transformer fleet can be optimized by limiting and spreading the yearly number of units to be replaced.
Financial and Regulatory Considerations
Having a clear understanding of the expenditure rules and regulations to apply for all kinds of intervention is important when considering the impact of an investment on the financial income statement and the revenues. For the financial consideration of all related costs chapter 2 gives the reader the basic tools to assess if an investment for life extension is worthwhile compared to a replacement. All relevant costs to be considered during a life extension process are:
- Costs of efficiency and losses
- Cost due to reduction of expected life span
- Costs of failures and business interruption
- Non-quantifiable costs
Screening of possible Candidates for Life Extension
Once the company strategy is in place and all regulatory and financial considerations are clear, the questions will be focused on the best candidate. A special focus is made on the aging mechanism of the insulation system as the functional end of life is commonly linked to the mechanical condition of the cellulose insulation. Understanding the role of moisture, temperature and oxygen as main ageing accelerating factors for all components is crucial to evaluate the effectiveness and potential success of a life extension measure. Chapter 3 details essential information for transformer anatomy and physiology and shows how to analyse common failures and degradation by applying existing diagnostic technics and helps structure the process from an observation to a technical conclusion.
Methods and Good Practices of Life Extension
The brochure shows the most relevant life extension methods, their technical benefit, related costs, and complexity. Major ageing mechanisms and life span reduction are mainly related to the insulation system and the components. The focus is, therefore, on the following:
- Oil treatment processes (e.g. oil treatment, filtering, reclamation, desludging, exchange)
- Active part drying processes and re-clamping
- Restore sealings and rust treatment
- Change and upgrade components (e.g. bushings, OLTC, cooler, protection)
- Complete refurbishment, including winding exchange
Furthermore, the survey and the nine real case studies give details and thoughts to consider when handling a life extension project.
Decision Making - Business Cases of Life Extension
The brochure assists asset managers in evaluating general life extension alternatives and strategies. The brochure presents a techno-economic analysis of some life extension alternatives, namely:
- Cellulose insulation drying
- Sealing the oil preservation system
- Enhanced cooling
- Enhanced reliability through replacement or refurbishment of components
- Mid-life refurbishment
By assessing the financial benefits of investment deferral and/or increased reliability and comparing them to the costs for each alternative through a Net Present Value calculation.
By addressing the typical set of questions, this Technical Brochure will support interested readers in covering all major steps when applying a methodology for life extension measures on their transformer and reactor. In addition, the multitude of referenced technical documents should enable the readers to get all the required knowledge and allow them to dive further into specific technical or economical topics if desired.