LPIT applications in HV Gas Insulated Switchgear
The acceptance of Low Power Instrument Transformer (LPIT) technology in GIS and process bus applications by utilities is growing continuously worldwide. The Technical Brochure of CIGRE Working Group B3.39 encourages utilities to evaluate the benefits and uses of LPIT technology. It assists to overcome potential barriers in the transition from conventional measurement technologies to LPIT through examples of successful long-term installation in utilities.
Convenor
(CH)
R. LUESCHER
Secretary
(FR)
G. VALEMBOIS
K. POHLINK (DE), H.-D. SCHLEMPER (CH), E. SPERLING (CH), W. OLSZEWSKI (DE), M. HYVÄRINEN (FI), G. GRANELLI (FR), Y. HIRATA (JP), T. ROKUNOHE (JP), D. DERMOT (IE), Z. QASTALANE (FR), C. FLAHAUT (FR), T. MORI (JP), R. ELOY (ES), M. SAITO (JP), M. MANDLIK (IN), A.M. AHLI (AE)
Corresponding Members: C. JONES (GB), J. BOEHM (AU), D. TABAKOVIC (US)
One benefit from the use of LPIT solutions is being able to provide for the requirements of protection applications and enough accuracy for metering functionality at the same time. The accumulated long time experience and significant number of reference installations show, that these solutions are now state of the art and adoption on a wider scale is predicted.
Another reason is matured standardisation. Relevant IEC standards for LPITs and Merging Units as well as for the communication are the basis for future-proof and interoperable devices. The new series IEC 61869, replacing IEC 60044, published or due to be published at the time this brochure was prepared, is presented in the following table.
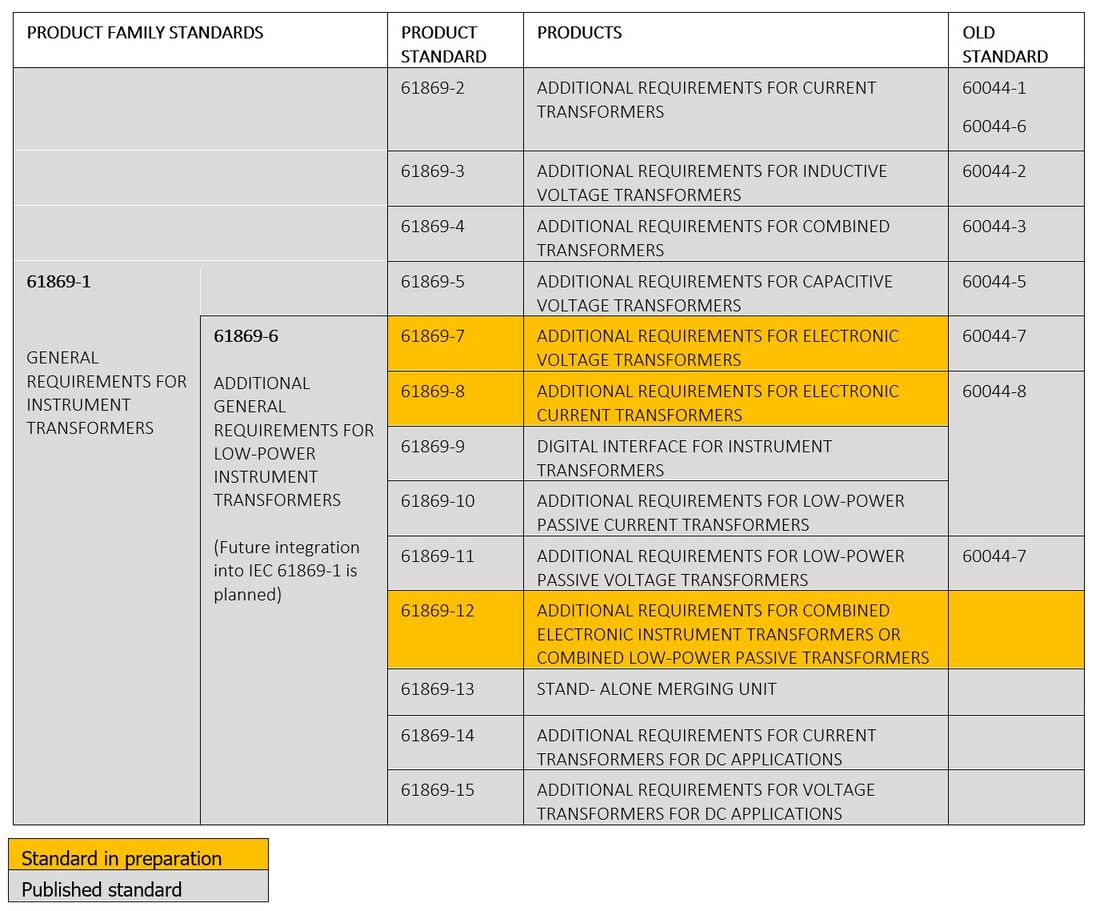
Table 1 - Structure of IEC 61869 series
Most common LPIT sensor technologies for GIS use Rogowski Coils for measurement of current and sensors with capacitive measurement principles for measurement of voltage. Moreover, sensors using optical measurement principles are also available.
The Gas Insulated Switchgear will gain a variety of advantages by using LPIT modules, e.g. more compact switchgear design, lower GIS weight, reduced amount of insulation gas and copper cabling. GIS configurations and traditional protection schemes can be simplified. LPITs with their low-power output offer improved product safety and security for substation personnel.
This Technical Brochure also emphasizes that the usage of LPITs leads to several consequences and changes for utilities in respect of the technical equipment, of the personnel and the procedures in substation operation. Replacement of electronics in GIS lifetime must be considered.
Scope
This Technical Brochure is divided into four main parts: Introduction, LPIT technologies for GIS, Requirements and Implementation, see Figure 1.
Figure 1 - TB structure
- INTRODUCTION explains the designations of LPITs in the series of IEC standards.
- LPIT TECHNOLOGIES for GIS summarizes suitable measuring principles for measurement of current and voltage for GIS or GIL applications. An overview of their bandwidth behaviour and comparison of connected burden values is provided along with details of the advantages and disadvantages of existing LPIT technologies.
- REQUIREMENTS part describes relevant drivers for the use of LPITs. This part puts forward the:
- technical criteria such as increased reliability, immunity to saturation;
- safety and environmental aspects with increased safety of operators, the reduced use of insulating gas;
- economic criteria, like costs of investment over the lifetime and savings resulting from the design and technology of LPITs;
- LPITs lifetime and lifecycle management with respect to the reliability, availability, impact of failure, repair, safety and security aspects are reviewed.
- The maintenance cycle which is seen as a major difference between conventional instrument transformers and LPITs is discussed;
- An overview of regulatory aspects for tariff metering is also provided. It is notable that the regulations for Current Transformers and Voltage Transformers for revenue or tariff metering can vary by country throughout the world. Standardisation work is currently in progress through various industry groups and described here for informative purposes.
- The IMPLEMENTATION part of the brochure introduces:
- The technical aspects important for the applications of LPITs in GIS for protection, control, measurement, metering and for power-quality metering. Most LPITs cover a large dynamic range with high precision accuracy and are suitable for revenue metering, measurement and protection at the same time. The requirements for LPITs in GIS to fulfil the same electrical, thermal, mechanical and environmental requirements according to IEC 62271-203 or similar is set out.
- The impact of LPITs and optimized GIS architectures, on reduced size, weight and footprint of the switchgear, but also with simplified voltage detection systems, are presented. Comparison of single line diagrams realised with conventional and non-conventional measurement technology shows further possibilities for the reduction of the number of GIS modules. Furthermore, the impact on the engineering processes and changes in the installation and commissioning practices are presented.
- The performance and experience of the currently used technologies for LPITs in pilot or regular projects are presented. A list of references with LPITs shows projects realised by European and Asian GIS manufacturers from 1990s until today. Application examples describe details of realisations in high voltage substations. Future-safe solutions due to harmonised IEC standards, interoperable LPIT products available from the main GIS manufacturers, reduced engineering and maintenance should increase the interest of users in low power instrument transformer technologies.
- The brochure also recommends limits for the testing of crosstalk effects (mutual influence) between phases of the three-phase GIS system. Furthermore, a list of electrical and environmental tests for the merging unit and a scheme for LPITs site testing are provided.
- A recommendation for the structure and documentation of LPIT product (user manual) is provided, to be used for project specific documentation and short datasheet leaflets.
- It can be established, that the use of LPITs and their application is growing. Their use for protection purposes are well established. They are currently available for metering applications; however, the implementation of commercial metering applications will require some additional efforts in the future to allow broader acceptance and compliance with regulatory aspects.
Conclusion
This Technical Brochure emphasize that the usage of LPITs leads to several consequences and changes for utilities in respect of the technical equipment, of the personnel and the procedures in substation operation. Replacement of electronics in GIS lifetime must be considered.
Several recommendations for LPIT applications are proposed:
- Type and routine testing should cover both the digital output signal and electronics in the measurement chain.
- Documentation should contain the settings for the digital communication interfaces, and details of the measuring technology used.
- Procedures for engineering, installation, commissioning and maintenance of LPITs in GIS must be adapted and verified. Utilities staff must be trained to work with tools and equipment suitable for LPITs.
- Devices for protection, metering and power quality analysis installed in substations with LPITs must be equipped with digital inputs for processing of sampled values provided by the Merging Unit. Together with communication via the process bus, these devices will be part of the digitalization concept of the substation.
- Revenue metering requires verification of the local regulations.
Future activities should include:
- Establishing of the regulatory aspects and guidelines for metering applications of LPIT sensors. Today these regulations are being decided on the national level of each specific country, so the general “working instruction” for metering functions cannot be provided today.
- IEC (e.g. missing parts in IEC 61869-x series) and IEEE standards (IEEE 1588) with focus on LPITs, Merging Unit and process bus applications must be completed and published.





